 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free! Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
 Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !
Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !  Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
Immunotherapy is a type of biological therapy that can enlist and strengthen the power of a patient's immune system to attack tumors, including immune checkpoint inhibitors, immune system modulators, treatment vaccines and adoptive cell therapy. Adoptive cell therapy (ACT), is a form of treatment that uses the cells of our immune system to eliminate cancer. Some of these approaches involve directly isolating our own immune cells and simply expanding their numbers, whereas others involve genetically engineering our immune cells (via gene therapy) to enhance their cancer-fighting capabilities.Currently, ACT mainly includes tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL), T cell receptor chimeric T cells (TCR-T) and chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR-T). Due to its significant advantages such as good curative effect, low toxic and side effects, and low drug resistance, immune cell therapy technology is determined as the "fifth pillar" of cancer treatment after traditional surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and monoclonal antibodies.
CAR-T cell therapy is advanced the furthest ACT in clinical development so far with nearly 1,300 clinical trials worldwide that have proved its great advantages in hematological tumors treatment. However, its therapeutic effect on solid tumors is limited. Different from hematomas, solid tumors can build the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment (TME), preventing the transport of immune cells and the infiltration of T lymphocytes to tumors. The immune response of some infiltrated T cells may still be restricted by immunosuppressive cells or inhibitors in the TME. In addition, the high heterogeneity of solid tumors would also limit the efficacy of CAR-T therapy targeting a single antigen.(more details could be found blow)
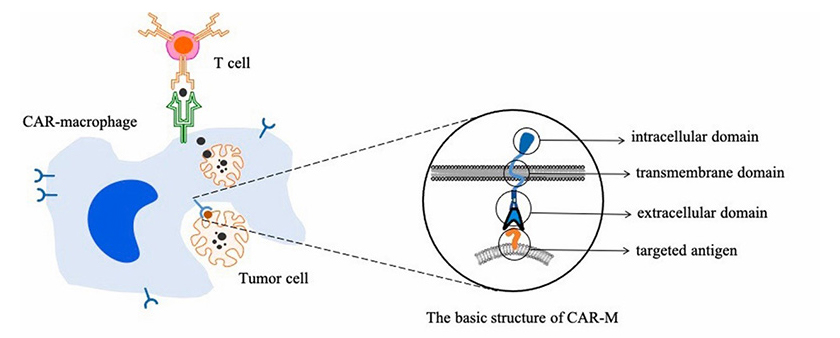
Figure 1. Targeted phagocytosis of cancer cells by CAR-macrophages and activation of T cells-mediated adaptive immune response
Considering the advantages and limitations of CAR-T cell therapy, scientists tried to modify other engineered CAR immune cells to overcome the limitations of CAR-T therapy for solid tumor treatment. CAR-macrophages (CAR-M) are considered as a promising type among immune cells. Macrophages can activate lymphocytes or other immune cells by engulfing cell debris and pathogens and presenting antigens, inducing the immune response to pathogens. In the tumor microenvironment, macrophages are the innate immune cells with the highest infiltration rate and can interact with almost all cellular components in TME, stimulate angiogenesis, increase tumor invasion, and mediate immunosuppression (1).(more details could be found blow)
Tumor-associated macrophages (TAM) are often classified as pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages or anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages. The M1-like phenotype is induced by toll-like receptor ligands or Th1 cytokines, heaving high antigen presenting capacity and being associated with microbicidal and pro-inflammatory activities. Therefore, they are termed as the “fight” macrophages and are associated with good prognosis in cancer context. In contrast, M2-like macrophages are polarized by Th2-derived cytokines. They are known as the “repair” or “fix” macrophages as they promote tissue repairviaimmune tolerance and tissue remodeling, debris scavenging and immune modulation. When it comes to cancer, M2-like macrophages favor tumor growth by supporting angiogenesis and expressing immunosuppressive molecules (4).
Macrophages, the body's first responder to viral infections, was considered as a potential direction for cell therapy. However, due to the difficulty of transfecting, attempts to attack cancer through modified macrophages cells have stalled. Until March 18 in 2021, Carisma Therapeutics (hereinafter referred to as Carisma) announced the completion of the first patient administration of CAR-M therapy (CT-0508), marking the treatment of solid tumors enter a new era.(more details could be found blow)
The genetic engineered CAR-M cells made by Carisma can express chimeric antigen receptors targeting Her2 antigen and are activated and differentiated into pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages. Therefore, the modified CAR-M cells can not only targeted phagocytize tumor cells, but also secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines to change the microenvironment around the tumor, and present tumor antigens to T cells to activate its immune response.
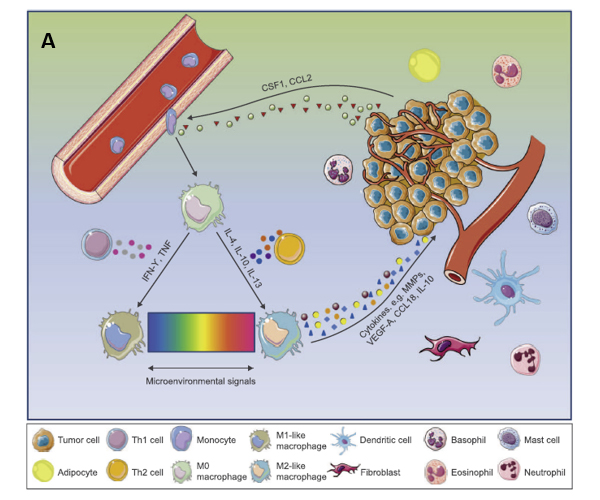
Figure 2. A: TME promotes phenotypic differentiation of tumor-associated macrophages. B: Illustration of how M1 and M2 TAMs are activated.
According to the preclinical research of Crisma, CAR-M therapy may overcome the challenges encountered by T cell therapy in the treatment of solid tumors.
In in vitro experiments: CAR-M cells showed antigen-specific phagocytosis and tumor clearance effects. In addition, it was effective for both Her2-positive and -negative tumors, functionally like in situ tumor vaccines.
In solid tumor xenograft mouse models: A single infusion of CAR-M can significantly reduce tumor burden and prolong overall survival (Figure 3).
In humanized mouse model: CAR-M can induce the production of pro-inflammatory tumor microenvironment and enhance the activity of anti-tumor T cells. In the presence of immunosuppressive cells, it can still lead to tumor regression.
The cell viability characterization: CAR-M can express pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, convert M2 type macrophages to M1, up-regulate the antigen presentation, recruit antigens and present them to T cells and resist the role of immunosuppressive cytokines (5).
In the process of in vitro verification of CAR-M phagocytosis experiment, Carisma used ACROBiosystems’ biotinylated protein, and the experimental results are consistent with the cell verification results (Figure 4 & 5).
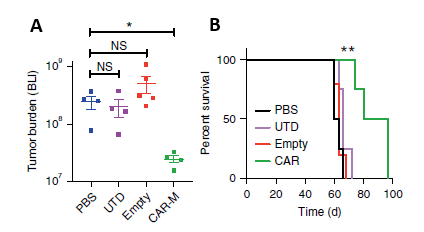
Figure 3. A: CAR-M treated mice demonstrated a marked reduction in tumor burden; B: CAR-Ms conferred a prolongation of overall survival.
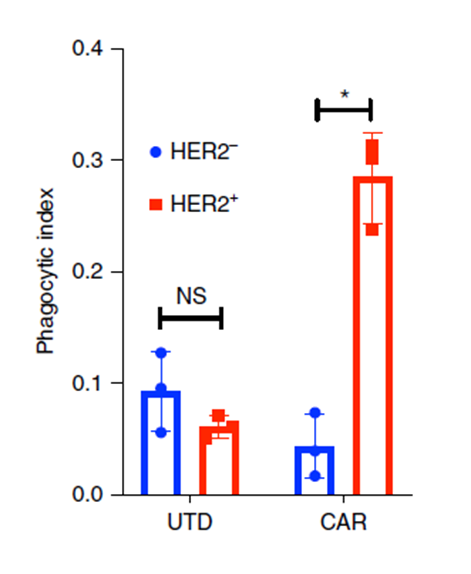
Figure 4. Incucyte-based phagocytosis of HER2 functionalized or control pH-Rodo-labeled beads by UTD or CAR-M.
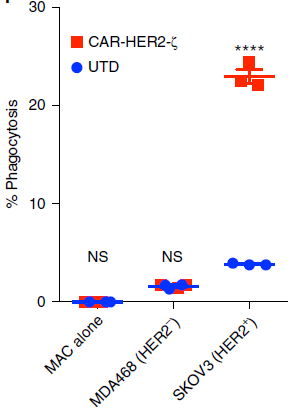
Figure 5. FACS-based phagocytosis of HER2− (MDA-468) or HER2+ (SKOV3) target tumor cells by UTD or CAR-M.
In words, although CAR-M therapy is novel and still has many challenges before entering clinical trials, it has demonstrated significant advantages in solving the problem of solid tumor treatment.
ACROBiosystems developed a variety of solid tumor-related biotinylated proteins and relevant cytokine proteins with high biological activity verified by multiple assay platforms such as ELISA,SPR, and FACS, assisting the development of CAR-M cell therapy and accelerating the R&D progress. You may need the proteins for:
Effect verification of macrophage-related antibodies’ ADCP (antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis)
CAR-M in vitro clinical verification
Stimulate the polarization of the macrophage M1/M2 phenotype
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Species | Product Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Her2 | HE2-H82E2 | Human | Biotinylated Human Her2 / ErbB2 Protein, His,Avitag™ |
| Her3 | HE2-C82E3 | Cynomolgus | Biotinylated Cynomolgus Her2 / ErbB2 Protein, His,Avitag™ (MALS verified) |
| PSMA | PSA-H82Qb | Human | Biotinylated Human PSMA / FOLH1 Protein, His,Avitag™ (active enzyme) |
| Mesothelin | MSN-H82F6 | Human | Biotinylated Human Mesothelin / MSLN (296-580) Protein, Fc,Avitag™ |
| Mesothelin | MSN-H82E9 | Human | Biotinylated Human Mesothelin / MSLN (296-580) Protein, His,Avitag™ (MALS verified) |
| CD19 | CD9-H82E9 | Human | Biotinylated Human CD19 (20-291) Protein, His,Avitag™ (SPR verified) |
| EGF R | EGR-H82E3 | Human | Biotinylated Human EGF R Protein, His,Avitag™ (MALS verified) |
| EGFRvIII | EGR-H82E0 | Human | Biotinylated Human EGFRvIII Protein, Avitag™,His Tag (MALS verified) |
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Species | Product Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| IFN-gamma | IFG-H4211 | Human | ActiveMax® Human IFN-gamma / IFNG Protein, Tag Free |
| IL-4 | IL4-H4218 | Human | ActiveMax® Human IL-4 Protein, Tag Free |
| IL-13 | IL3-H52H4 | Human | Human IL-13 Protein, His Tag |
| M-CSF | MCF-H5247 | Human | Human M-CSF / CSF-1 Protein, His Tag |
| LIF | LIF-H521b | Human | ActiveMax® Human LIF Protein, Tag Free |
| IL-10 | IL0-H4248 | Human | Human IL-10 Protein, His Tag |
| TGF-beta 1 | TG1-H4212 | Human | ActiveMax® Human TGF-Beta 1 / TGFB1 Protein, Tag Free |
| IL-6 | IL6-H4218 | Human | ActiveMax® Human IL-6 Protein, Tag Free |
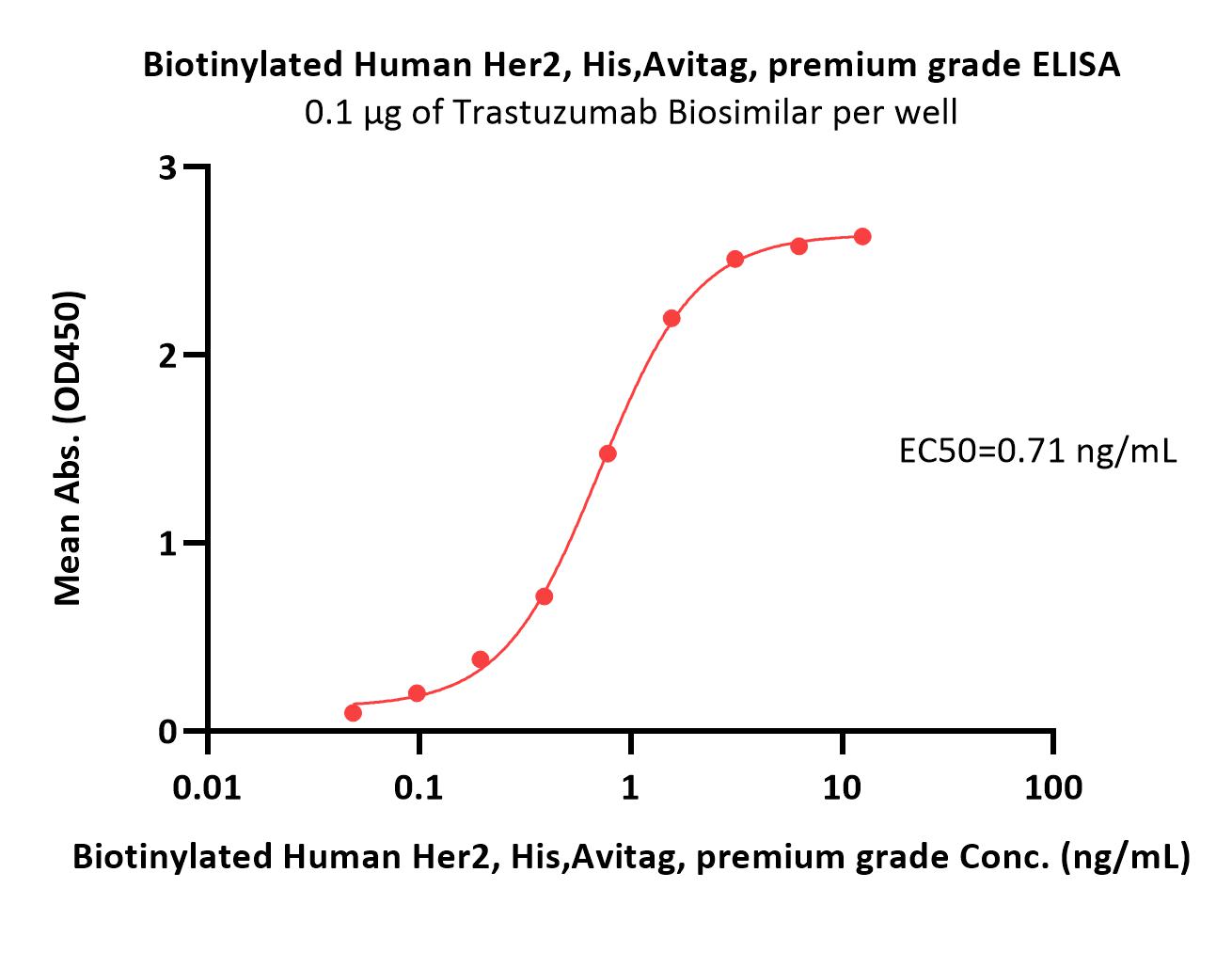
Immobilized Trastuzumab at 3 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Biotinylated Human Her2, His,Avitag (Cat. No. HE2-H82E2) with a linear range of 0.2-6 ng/mL (QC tested).
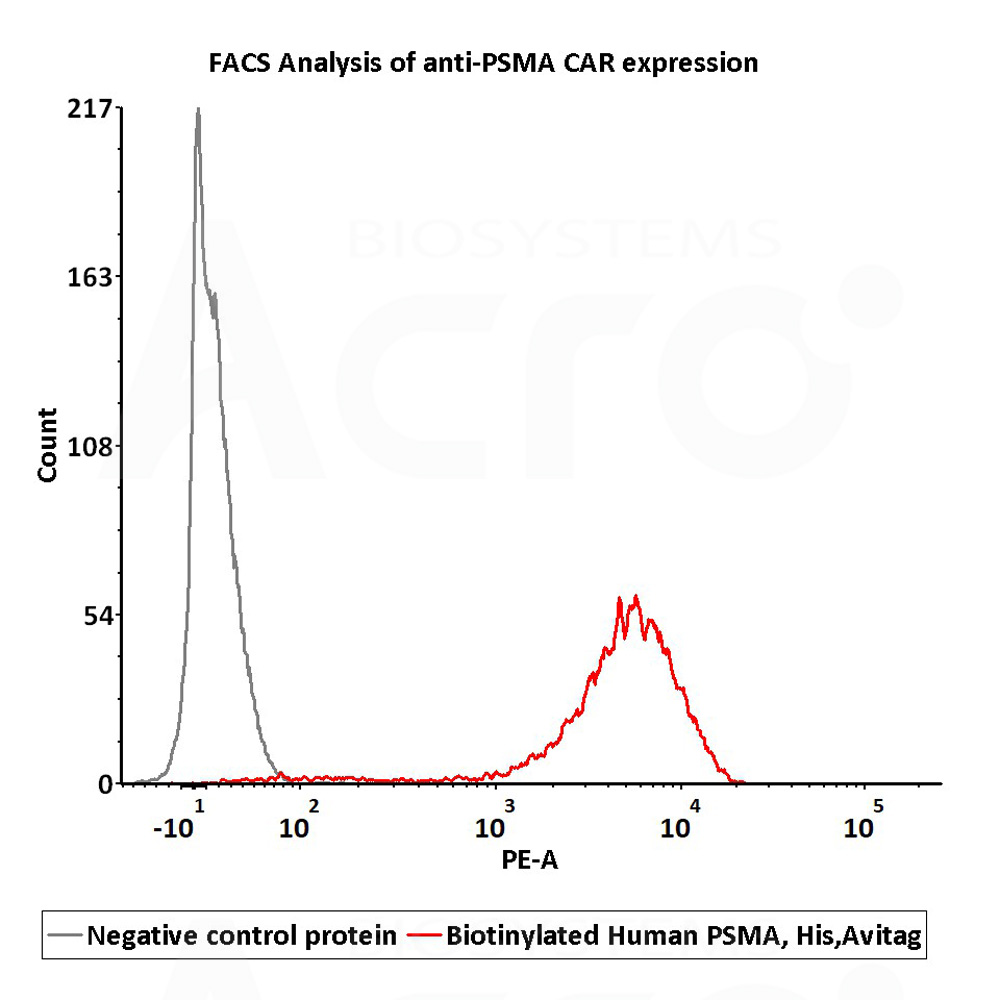
2e5 of PSMA-CAR-293 cells transfected with anti-PSMA-scFv were stained with 100μl of 1μg/mL of Biotinylated Human PSMA, His,Avitag (Cat. No. PSA-H82Qb) and negative control protein respectively, washed and then followed by PE-SA and analyzed with FACS (Routiney tested).
More articles and related documents about CAR-M for free~
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.
