 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free! Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
 Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !
Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !  Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
> Cerebral-related Solutions & Services
Explore our ready-to-use brain organoids, cells, and services. Learn about how we can assist with disease modeling, organoid differentiation, and drug testing, encompassing cell activity assays and electrophysiological measurement platforms to provide reliable insights into neuroscience research.
With advancements in stem cell technology, brain models derived from induced pluripotent stem cells are a powerful tool for research. The ability to differentiate into various cell types such as neural cells, enables us to create three-dimensional models that mimic the structure and functions of the human brain. These brain models are particularly useful in advancing the understanding of neural development and studying neurological diseases.
Brain Organoids
Brain organoids are a miniaturized, in vitro version of the brain that is derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). These organoids are designed to have a similar cellular composition and architecture as the brain, exhibiting similar mechano-physiological and electrophysiological properties. As such, brain organoids are critical tools for researchers developing treatments to neurological diseases, driving different applications such as:

Neurological
Drug Screening
Neurological
Drug Screening
Organoid-based brain models provide a scalable, high-throughput drug screening assay for drug efficacy and toxicity.

Neurological
Disease Modeling
Neurological
Disease Modeling
Brain models are an alternative to animal models, providing a more physiologically relevant platform that models diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
AAV
Serotype Screening
AAV
Serotype Screening
Adeno-associated viruses are a critical gene delivery tool. Finding the right serotype for gene transduction into the target tissue type can make or break gene therapies.
Neurodevelopmental
Research
Neurodevelopmental
Research
Neurodevelopmental research strives to learn about the formation of the nervous system during development, such as generation, migration, connectivity and more.
Brain organoids and differentiation kits are available to support high-throughput differentiation of brain organoids from iPSCs.
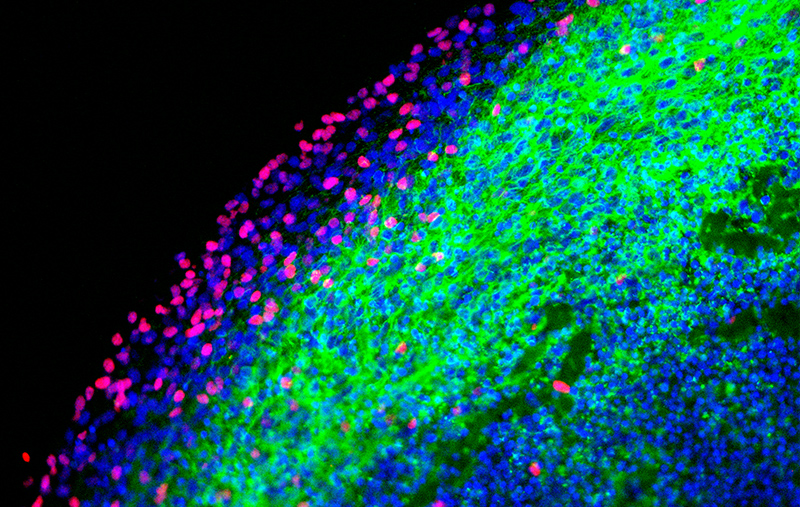
Immunostaining of 119-day old brain organoid for OLIG2 and TUJ1 reveals the distribution of oligodendroglia and mature neuron cells, respectively.
| Cat. No. | Description |
| CIPO-BWL001K | Ready-to-use Human iPSC-Derived Cerebral Organoids |
| CIPO-BWL002K | Ready-to-use Human iPSC-Derived Mature Cerebral Organoids 100 days+ |
| CIPO-MBWL001K | Ready-to-use Human iPSC-Derived Midbrain Organoids |
| CIPO-BWL001KC | Cryopreserved Human iPSC-Derived Cerebral Organoids |
| RIPO-BWM001K | Human iPSC-Derived Cerebral Organoid Differentiation Kit |
| RIPO-BWM003 | Human iPSC-Derived Cerebral Organoid Maturation and Maintenance Kit |
| RIPO-BWM006 | Cerebral Organoid Cryopreservation Kit |
Neural Cells
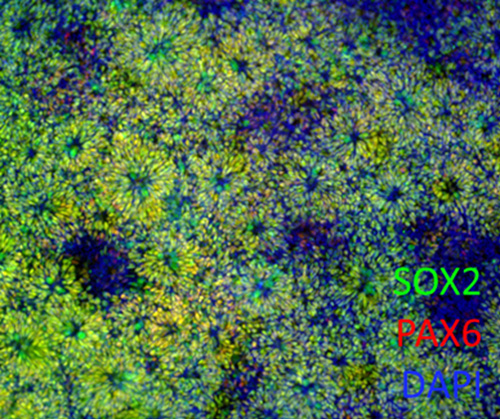
Neural progenitor cells are the progenitor cells that develop into glial and neuronal cells that populate the central nervous system. They possess the ability to self-renew and secrete neurotrophic factors that are crucial in promoting neural regeneration.
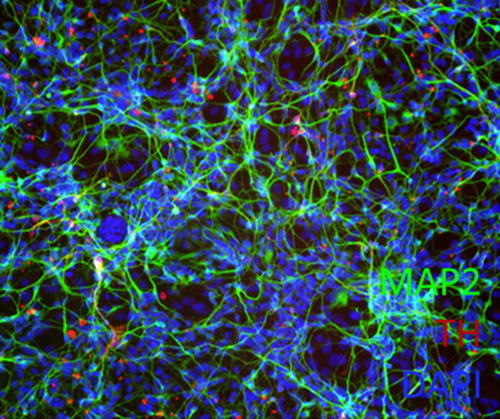
Neural progenitor cells are the progenitor cells that develop into glial and neuronal cells that populate the central nervous system. They possess the ability to self-renew and secrete neurotrophic factors that are crucial in promoting neural regeneration.
| Cat. No. | Description |
| CIPC-NDC001 | Human iPSC-Derived Neural Progenitor Cells (Parkinson's disease) |
| CIPC-DDC001 | Human iPSC-Derived Dopaminergic Neurons (Parkinson's disease) |
| CIPC-NWC001 | Human iPSC-Derived Neural Progenitor Cells |
| CIPC-DWC001 | Human iPSC-Derived Dopaminergic Neurons |
Brain Services
We offer differentiation services to develop brain organoids from iPSCs or human tissue. Organoids are validated by the expression of brain-related protein markers to ensure differentiation and maturity.
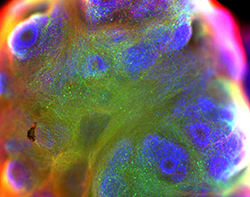
We can measure the inhibitory effect of electrical signals blocking drugs and the cell viability of neuron cells to better predict drug cerebral toxicity.
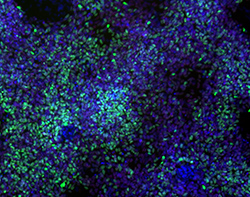
We can help to construct the AD/PD model with PFFs and provide corresponding pathological findings and biochemical evidence. At the same time, we can also provide you with follow-up drug screening services.
Interested? Leave a message!
Brain Case Studies
Developed using our organoid differentiation kit, 55-day old cerebral organoids derived from iPSCs were incubated with varying concentrations of Tau pre-formed fibrils. Anti-pTau antibodies were used to visualize Tau aggregation alongside MAP2 staining to visualize mature neurons.
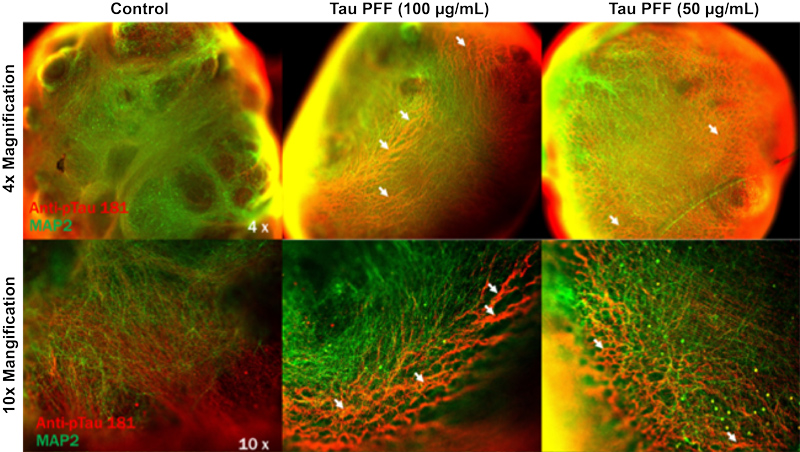
Aggregation of Tau was visualized in organoids incubated with Tau pre-formed fibrils, represented by the thickening of lines in red. Increasing concentration of PFFs resulted in a more noticeable aggregation of Tau.
Developed using our organoid differentiation kit, cerebral organoids derived from iPSCs were incubated with varying concentrations of α-synuclein pre-formed fibrils. TH staining was used to visualize dopaminergic neurons, with MAP2 representing mature neurons.
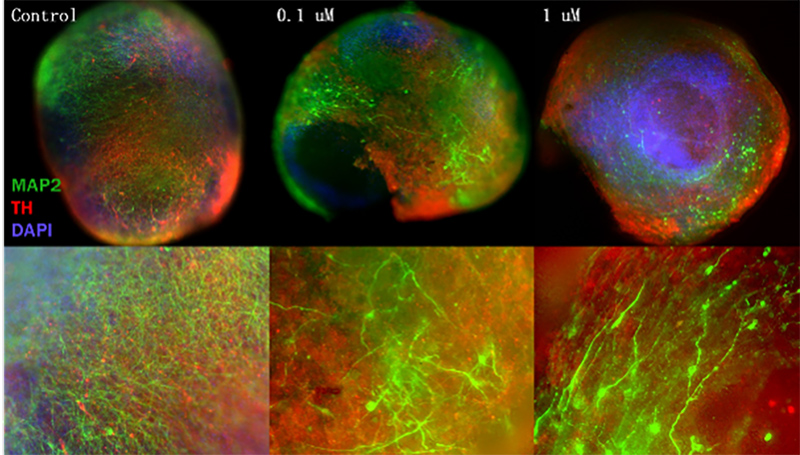
With the addition of α-syn PFFs into the organoid model, swelling of axon microtubules and neuron density loss is visualized. In comparison to control, significant microtubule loss (thin green lines) suggests oxidative stress stemming from addition of PFFs.
Several AAV serotypes were utilized to evaluate transgene efficacy using cerebral organoid models. Evaluation of the resulting expression of delivered GFP transgene was compared to evaluate transduction and select the optimal AAV serotype in comparison to commercial wild-type AAVs. Cerebral organoids grown for 101 days were infected with 1E+11 μg of AAV5-WT (left), IVB-1 (middle), and IVB-2 (right).
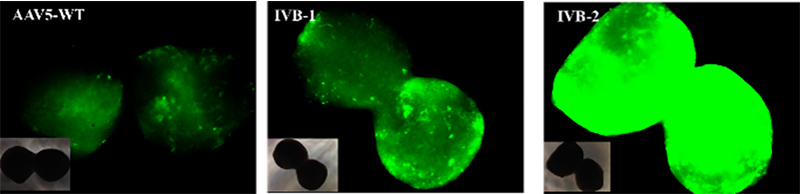
The IVB-2 subtype showed a significantly higher level of infectiousness revealed by the high levels of GFP expression in cerebral organoids.
Compared neuronal activity in organoid cultures between a control group and a group treated with Muscimol, a GABAA receptor agonist.
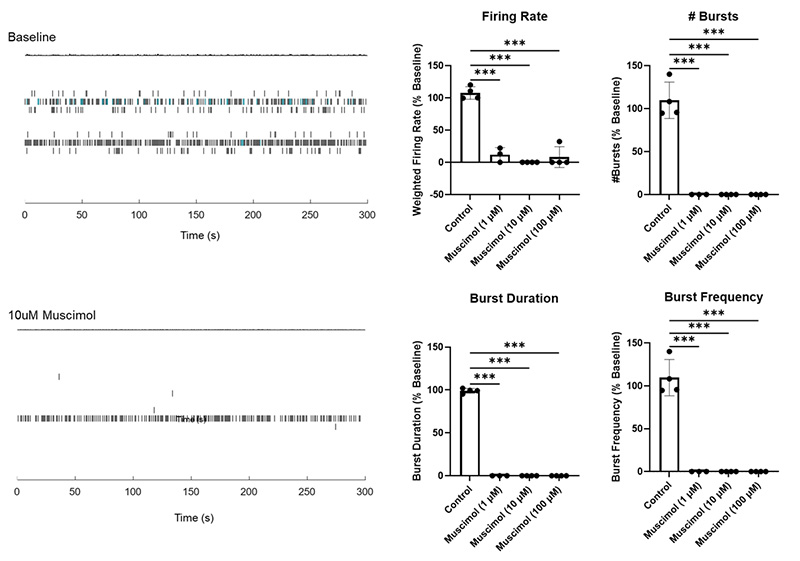
The control organoid (top) showed robust network burst activity and a high mean spike firing rate. In contrast, the Muscimol-treated organoid (bottom) exhibited decreased burst activity and a lower mean spike firing rate, indicating inhibitory modulation of neuronal excitability.
A subset of organoids was treated with Picrotoxin, a compound known to block GABAA receptor-mediated inhibition. Extracellular recordings were performed using multi-electrode arrays (MEAs) to monitor neuronal activity.
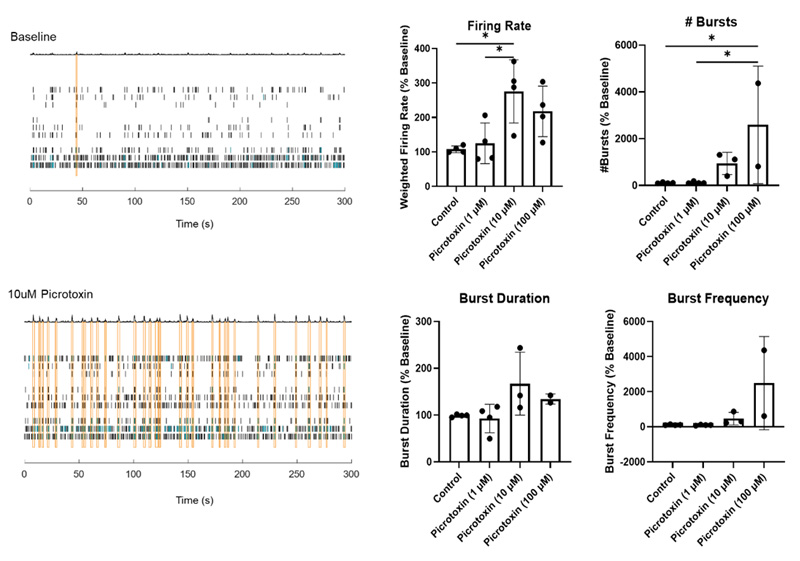
Picrotoxin-treated cerebral organoids showed synchronized bursting activity, an indicator of synaptic maturation.
>> Aneuro, Advance Neuroscience Research
References
1. Hernandez-Baltazar, Daniel, et al. "Animal model of Parkinson disease: Neuroinflammation and apoptosis in the 6-hydroxydopamine-induced model." Experimental Animal Models of Human Diseases [Internet]. Rijeka: InTech (2018): 375-393.
2. Chongyuan Luo, et al. Cerebral Organoids Recapitulate Epigenomic Signatures of the Human Fetal Brain. VOLUME 17, ISSUE 12, P3369-3384, DECEMBER 20, 2016.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.
