
Leave message
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Fill out this form to inquire about our custom protein services!
Inquire about our Custom Services >>

































 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free!
Offering SPR-BLI Services - Proteins provided for free! Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
Get your ComboX free sample to test now!
 Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !
Time Limited Offer: Welcome Gift for New Customers !  Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
Shipping Price Reduction for EU Regions
> Insights > The importance of N protein variants in antibody test and drug design Since the outbreak of the severe pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection, the spike protein (S) of the virus has been used as the leading target antigen in epidemiological studies, diagnostic tests and drug and vaccine development. Nucleocapsid protein (N), the structural protein that packages viral RNA into new virions, is identified a second important player in this life-or-death contest. A significant amount of studies demonstrated that the N protein is highly immunogenic and is expressed abundantly during infection, therefore suitable as a diagnostic reagent or antibody target.
Related article: S protein: key to the pandemic
Like spike protein, nucleocapsid protein is quite tolerant of mutations. This protein is divided into two main domains, the N-terminal RNA-binding domain (NTD) and the C-terminal dimerization domain (CTD), joined by a central serine/arginine-rich (SR)-linker. The NTD directly interacts with the viral RNA and is highly divergent. The CTD is important for eliciting antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 during an immune response. The SR-linker harbors phosphorylation sites critical for the modulation of nucleocapsid multimerization, translational inhibitory activity and cellular localization.
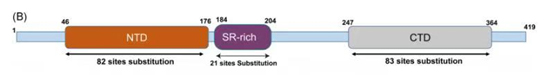
Figure 1. the structure of Nucleocapsid protein
Based on comprehensive studies of reported mutations, ACROBiosystems has developed multiple recombinant N protein variants. The co-occuring mutations R203K and G204R are most common with an estimated frequency of >60% in global sequences, which is comparable to the dominant D614G mutation on the spike protein. Other frequently occurred mutations include P13L, P80R, D103Y, S194L, etc.
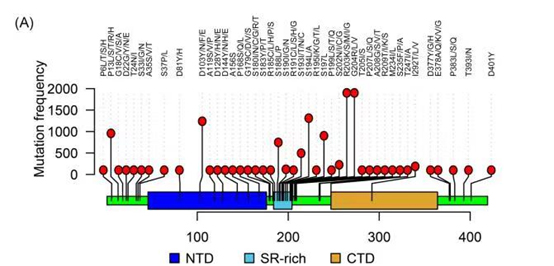
Figure 2. current reported mutations on the Nucleocapsid protein
Research into the specific functional consequences of these N protein mutations are currently limited. The availability of a panel of N proteins with high purity and bioactivity now paved your way to systematically examine its implication in antibody testing and drug design.
Assay Data
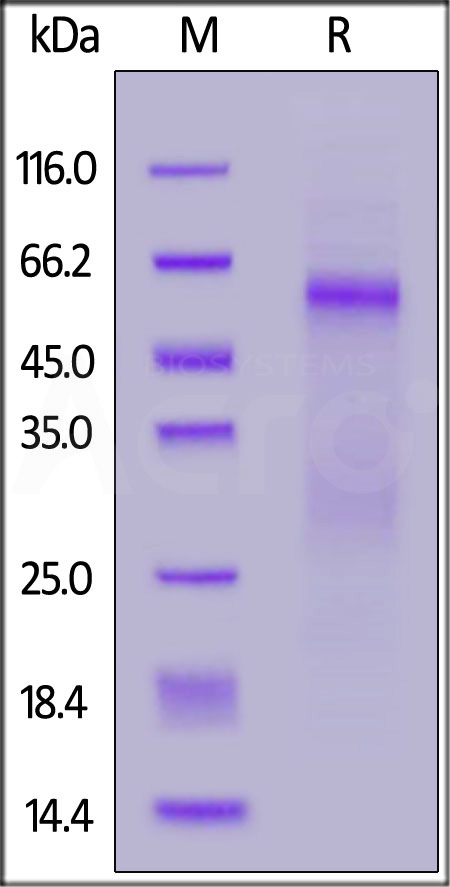
SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid protein, His Tag (Cat. No. NUN-C52H8) on SDS-PAGE under reducing (R) condition. The gel was stained overnight with Coomassie Blue. The purity of the protein is greater than 90%.
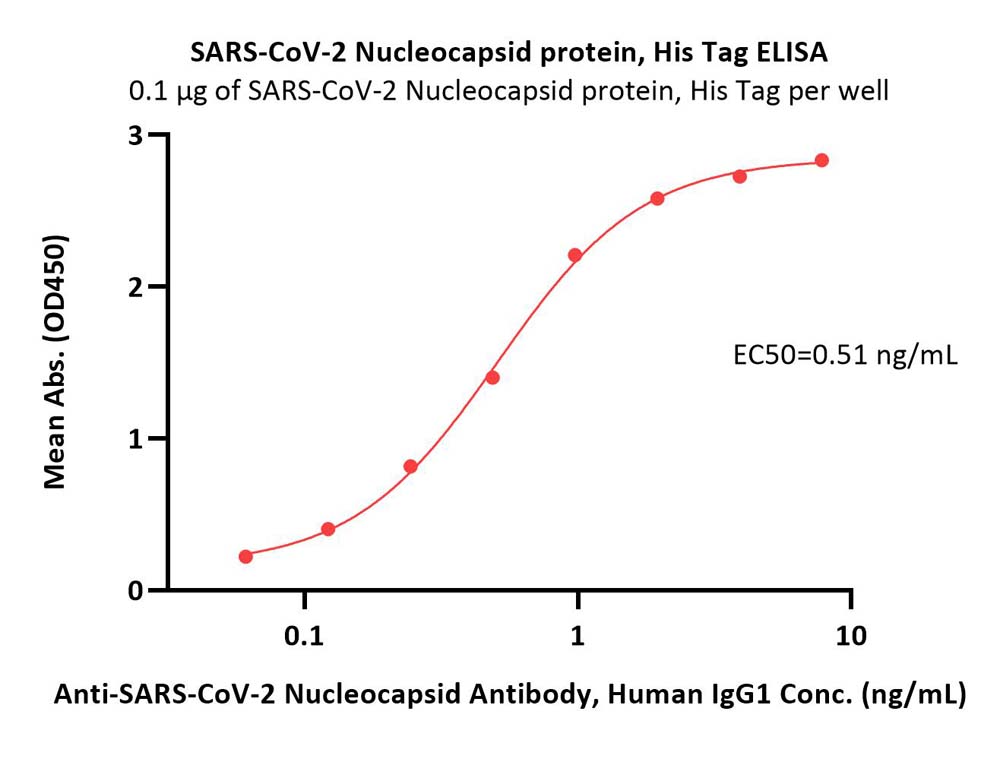
Immobilized SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid protein, His Tag (Cat. No. NUN-C52H8) at 1 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Antibody, Human IgG1 (Cat. No. NUN-S41A1) with a linear range of 0.06-1 ng/mL (QC tested).
reference
Ye, Q, West, AMV, Silletti, S, Corbett, KD. Architecture and self-assembly of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein. Protein Science. 2020; 29: 1890– 1901. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.3909
Troyano-Hernáez P, Reinosa R, Holguín Á. Evolution of SARS-CoV-2 Envelope, Membrane, Nucleocapsid, and Spike Structural Proteins from the Beginning of the Pandemic to September 2020: A Global and Regional Approach by Epidemiological Week. Viruses. 2021 Feb;13(2). DOI: 10.3390/v13020243.
Rahman MS, Islam MR, Alam ASMRU, et al. Evolutionary dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein and its consequences. J Med Virol. 2021 Apr;93(4):2177-2195. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26626. Epub 2020 Nov 10. PMID: 33095454.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.







